| HomeTurtlegraficsGPanelRoboticsGameGrid WebTigerPython |
| Python - Online |
| Deutsch English |
3. ACCELERATION SENSOR
![]()
YOU LEARN HERE... |
how you can use the acceleration sensor to detect changes in position and movements of the micro:bit. |
SENSOR VALUES |
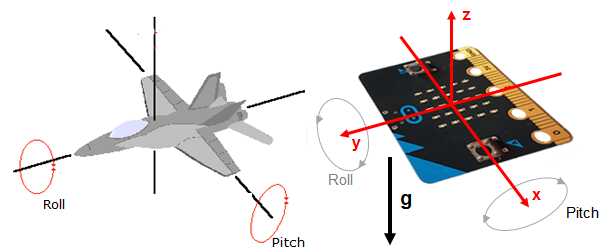
The micro:bit's acceleration sensor measures both the constant gravitational acceleration of around 10 m/s2, which points vertically downwards, and accelerations caused by movements.
It is similar to the attitude display of aeroplanes. If you tilt the board forwards or backwards, the pitch angle changes; if you tilt it sideways, the roll angle changes.
In the programme, you use the accelerometer object and call accelerometer.get_x(), accelerometer.get_y() or accelerometer.get_z(), which return values in the range from approximately -2000 to 2000, corresponding to accelerations of -20 m/s2 and 20 m/s2. With acceloremeter.get_values() you get back all three values in one tuple. |
EXAMPLES |
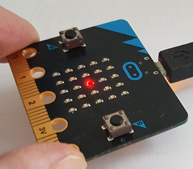
Query sensor values Start the programme below, tilt the micro:bit bit from the horizontal position to the left or down to the right and observe the sensor values that are written out in the terminal window.
Program: from microbit import * while True: acc = accelerometer.get_x() print (acc) if acc > 0: display.show(Image.ARROW_E) else: display.show(Image.ARROW_W) sleep(100)
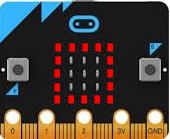
Only one pixel is displayed, which shifts to the right, left, up or down depending on the tilt. The aim is to align the level so that the centre LED lights up. In the programme, you use four conditions to determine the x and y values of the pixel and then delete the pixel before lighting the new one. Program: from microbit import * x = 1 y = 1 while True: accX = accelerometer.get_x() accY = accelerometer.get_y() if accX > 100 and x < 4: x += 1 elif accX < -100 and x > 0: x -= 1 elif accY > 100 and y < 4: y += 1 elif accY < -100 and y > 0: y -= 1 display.clear() display.set_pixel(x, y, 9) sleep(100) |
REMEMBER YOUR... |
| You can use the acceleration sensor to record the movements and position of the micro:bit. The sensor values are usually scanned regularly every 10 - 100 milliseconds in a measuring loop. This is also known as polling the sensor values. |
TO SOLVE BY YOURSELF |
|
![]()
Note:
You can calculate the pitch and roll angles from the three acceleration components. Start the following programme and tilt the board sideways or forwards and backwards. The rotation angles are displayed in degrees in the terminal window.
from microbit import * from math import * def getPitch(): a = accelerometer.get_values() pitch = atan2(a[1], -a[2]) return int(degrees(pitch)) def getRoll(): a = accelerometer.get_values() anorm = sqrt(a[0] * a[0] + a[1] * a[1] + a[2] * a[2]) roll = asin(a[0] / anorm) return int(degrees(roll)) while True: pitch = getPitch() roll = getRoll() print("p: " + str(pitch)) print("r: " + str(roll)) print() sleep(100)