| HomeTurtlegraficsGPanelRoboticsGameGrid WebTigerPython |
| Python - Online |
| Deutsch English |
10. LIDAR, PID and LIGHTSensor (mbrobot plusV3)
![]()
YOU LEARN HERE... |
how to use the advanced functions of the mbRobot Plus V3. In addition to the functions described in the previous chapters, the latest Maqueen model Plus V3 has the following enhancements:
|
HOW DOES LIDAR WORK? |
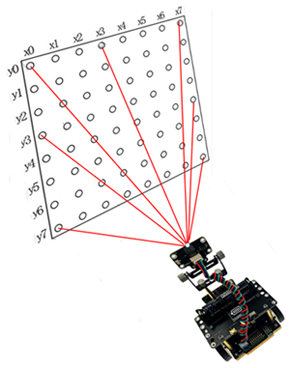
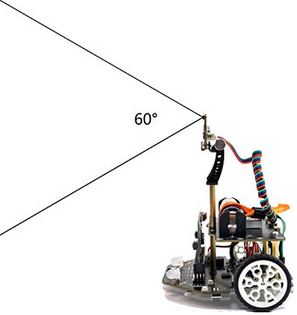
Maqueen Plus V3 is equipped with a matrix lidar sensor. Within a 60-degree detection range, it provides a matrix with 64 measured values.
You can use the following functions for distance measurement:
|
EXAMPLES |
Program: from mbrobot_plusV3 import * repeat: row = getDistanceRow(4) #8 Values left to right print(row) if row[0] < row[7]: setLEDLeft(1) setLEDRight(0) else: setLEDLeft(0) setLEDRight(2) delay(100) Example 3: What does the LIDAR sensor ‘see’?
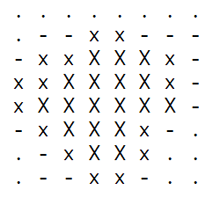
Program: from mbrobot_plusV3 import * def readData(): data = getDistanceList() matrix = [] for row in range(8): rowData = [data[row * 8 + col] for col in range(8)] matrix.append(rowData) return matrix def showMap(matrix): for row in matrix: line = "" for val in row: if val < 30: line += " X " elif val < 60: line += " x " elif val < 100: line += " - " elif val < 150: line += " . " else: line += " " print(line) print("") print("------------------------------") print("") while True: matrix = readData() showMap(matrix) delay(3000) |
PID CONTROL |
Maqueen Plus V3 has a motor encoder that allows you to precisely control the robot's forward movement and steering angle. |
EXAMPLE |
EXAMPLE 1: Driving and turning with PID control Program: from mbrobot_plusV3 import * pidControlDistance(1, 20, 1) pidControlDistance(2, 20, 1) pidControlAngle(90, 1) pidControlAngle(-90, 1) pidControlDistance(1, 20, 1) : the robot moves 20 cm forward. |
LIGHT INTENSITY SENSORS |
The changes in resistance are detected by the micro:bit and converted into a digital value in the range from 0 to 1023, where 0 means very dark and 1023 means very bright. The sensors are located at the front left and right of the chassis. |
MEXAMPLE |
Controlling robots with a torch
readLightIntensity(0) gives the light value of the right sensor. You may need to adjust the threshold value of 250 to suit the ambient brightness. Program: from mbrobot_plusV3 import * setSpeed(30) repeat: vR = readLightIntensity(0) #right vL = readLightIntensity(1) #left print(vR, vL) if vR > 250: rightArc(0.2) elif vL > 250: leftArc(0.2) else: forward() delay(100) |
INTERSECTION DETECTION |
mbRobot Plus V3 detects intersections: T-junctions, left-turn, right-turn and straight intersections. The intersectionDetecting() function returns 1 if the robot detects an intersection, otherwise 0. |
EXAMPLE |
Program: from mbrobot_plusV3 import * forward() repeat: if intersectionDetecting(): stop() delay(100) |
REMENBER... |
The Lidar sensor measures the distance to objects in front of it and provides a matrix with 64 measured values. Depending on the problem, you can use just one value, a list of values in a row, or a list of all 64 measured values. With PID Control, you can move the robot forward or backward by a precise distance (in centimetres) or rotate it by an angle. The light sensors allow you to measure the intensity of the ambient light. The measured values range from 0 to 1023. You will get higher values especially when you shine a torch on the sensors. The intersectionDetecting() function returns 1 when the robot is at an intersection. To determine the type of intersection, it is best to use the irL2 or irR2 infrared sensors, which can detect the brightness of the surface next to the lane. |
TO SOLVE BY YOURSELF |
|
![]()